“DeepLab”の初出とその直後に出た論文. 最新のDeepLabv3は現在のstate-of-the-artである.
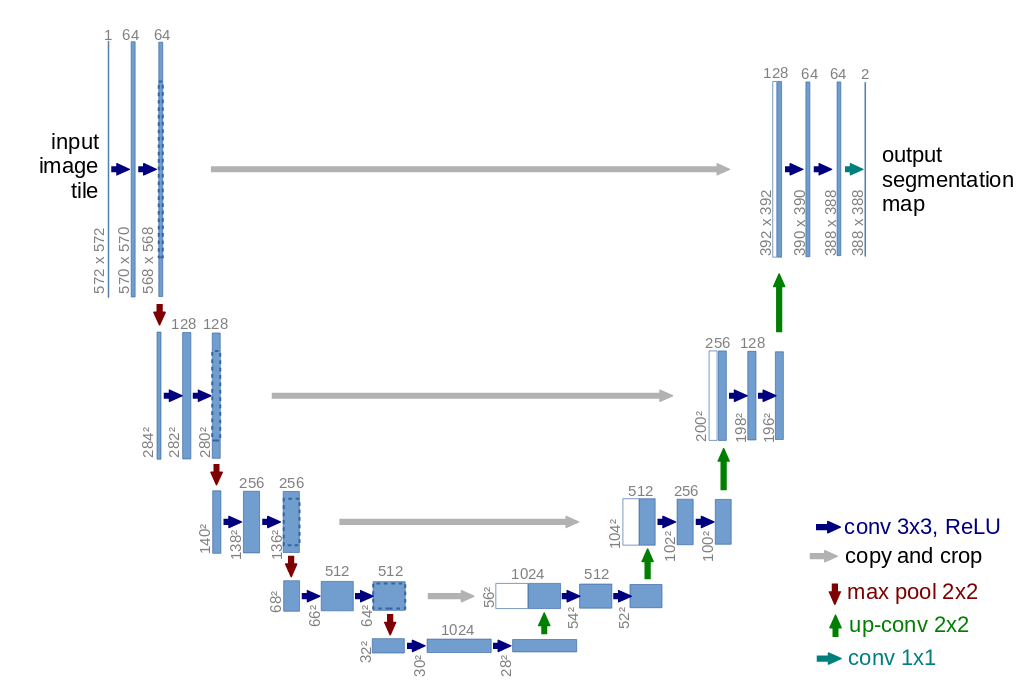
DeepLabの特徴を3つ挙げる.
1. poolingによるdownsamplingのかわりにAtrous Convolution(fig.1)を使って,downsamplingのときに得られる一つ一つの特徴量がより広い範囲の入力元を反映することになる.Atrous ConvolutionはDilated Convolutionとも呼ばれる. PyTorchではtorch.nn.Conv2dのdilation引数で設定できる.
 figure 1. from vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic
figure 1. from vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic
2. 画面いっぱいに写っていようと画面の片隅に写っていようと猫は猫であるように,image segmentationではscale invarianceを考慮しなければならない. 著者はAtrous Convolutionのdilationを様々に設定することでこれに対処している(fig.2). 著者はこの技法を”atrous spatial pyramid pooling”(ASPP)と呼んでいる.

figure 2, from Liang-Chieh et al. 2016
3. bilinaer upsamplingによってfeature mapを引き伸ばすのだが,その直後にfully-connected Conditional Random Field (CRF)を用いる. CRFはdeep-learning以前のimage segmentationでよく用いられてきた技法である.画像の隣り合った画素のペアを考えて,その2つが同じobjectに入るか否かを計算していくのがUnary(Basic) CRFである(fig.3a). Fully Connecetd CRFでは文字通りある画素とその他の任意の画素のペアが同じobjectに入るか否かを考慮する(fig.3b). 当然Fully Connected CRFはそのままだと極めて計算量が大きいが,Krahenbuhl and Koltun, 2011.は平均場近似を導入して高速化を行い,exhaustiveな計算に近い結果を得た(fig.4).

figure 3. from https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/courses/compsci708s1c/lectures/glect-html/topic4c708fsc.htm

figure 4, from Krahenbuhl and Koltun, 2011
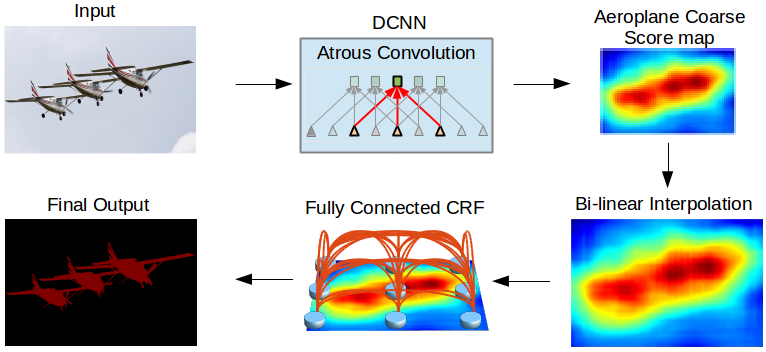
モデル概観, from Liang-Chieh et al. 2015
似たアーキテクチャで注目されているのにZheng et al. Conditional Random Fields as Recurrent Neural Networksがある.
(詳しい議論はDeepLabv3の論文読みで)
 figure 1, SegNetウェブサイトより
figure 1, SegNetウェブサイトより